香农理论中,最重要的部分就是entropy的概念。Entropy曾经是波尔兹曼在热力学第二定律引入的概念,用来衡量一个系统的能量有多少被用来作为有用功,有多少可能转化为无效的热量。从分子运动论的观点看,作功是大量分子的有规则运动,而热运动则是大量分子的无规则运动,因此entropy也可以理解为分子运动的混乱程度。在信息论中,entropy被引申用来衡量随机变量的不确定程度。
众所周知,物体的重量可以用天平来衡量,物体的热量也可以用焦耳等单位来测量。可是对于文字,声音和视频,这些乘载信息的媒介,可不可以用一种统一的方式来衡量这些媒介的信息量。香农entropy的作用就是用来衡量一段媒介中所包含信息量的平均大小。例如,中文entropy是9.65比特,英文entropy是4.03比特。这表明中文的复杂程度高于英文,反映了中文词义丰富、行文简练,但处理难度也大。同时,香农entropy也代表了一段信息能够被无损压缩的上限值。
香农定义了一个独立随机变量
\[H(X)=E(I(X))\]其中,\(E\)是\(I\)的期望,\(I\)是X的自信息量,也就是所谓的self-information。
衡量一个自信息量self-information的大小必须满足以下几个条件:
1.一个随机变量\(x_{i}\)的信息量只依赖于这个随机变量\(x_{i}\)的概率\(p_{i}\),与它本身的内容是没有关系的,其中:
\[\sum_{i=1}p_{i}=1\]
2.Self-information是一个\(p_{i}\)的连续函数。
3.Self-information是一个\(p_{i}\)的减函数。
4.如果\(p_{i}=p_{i,1}*p_{i,2}\),那么\(I(x_{i})=I(x_{i,1})+I(x_{i,2}).\)
符合以上条件的只有“logarithmic”函数,因此self-information可以定义为:
\[I(x_{i})=-log(P_{i})\]
因此Entropy可以定义为:
\[H(X)=\sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_{i})I(x_{i})=-\sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_{i})log_{b}p(x_{i})\]
其中,b是对数logarithm的底。当\(P(x_{i})=0\)的时候,\(0log_{b}0\)被定义为等于0,与其极限条件一致:
\[ lim_{p \rightarrow 0+}
plog_{b}p = 0\]
如果对数log以2为底,计算出来的Entropy就是以bit为单位。而在计算机和数字通信领域,也都是以2进制作为基本单位,所以Entropy的概念可以被广泛的应用到计算机和通信领域。Self-information(信息量)可以被定义为随机不确定程度的减少,换句话说,信息是用来减少随机不定性的变量,也就是信息是确定性的增加。
假设一个独立随机变量X有四个可能的值\({A, B, C, D}\), 它们的分布为:
\[P(X=A)=1/4, P(X=B)=1/4, P(X=C)=1/4, P(X=D)=1/4\]
一个字符序列:BAACBADCDADDDA..符合上面的分布:
我们要把这段字符用二进制的通道传输出去,可以把这四个字符分别编码为(A=00, B=01, C=10, D=11)。
0100001001001110110011111100...
平均每个字符需要2bits来传输
如果这四个值的概率分布不是一样的,新的分布如下:
\[P(X=A)=1/2, P(X=B)=1/4, P(X=C)=1/8, P(X=D)=1/8\]
如果我们把编码变成(A=0, B=10, C=110, D=111),
每个字符的平均长度会变成: 1/2*1+1/4*2+1/8*3+1/8*3=1.75bits
如果给定的一个随机变量\(X={V_{1}, V_{2}, ..., V_{m}}\)的分布,
\[P(X=V_{1})=p_{1}, P(X=V_{2})=p_{2}, ..., P(X=V_{m})=p_{m}\]
基于X的分布,每个字符需要编码成最小的比特数是什么?答案就是随机变量Entropy的大小。
\[H(X)=-p_{1}log_{2}P_{1}-p_{2}log_{2}P_{2}-..-p_{m}log_{2}P_{m}=-\sum_{j=1}^{m}p_{j}log_{2}p_{j}\]
如果随机变量\(X\)的Entropy的值越大,说明这个随机变量\(X\)不确定程度越大,需要把它编码成二进制代码量也越大。从上面的例子可以看出如果随机变量的分布越是不对称,其Entropy值也越小,也意味着这个随机变量可预测性也相对来说较高。
在介绍Information Gain之前,必须先介绍以下Canditional Entropy(条件熵)\(H(Y|X=v)\)的概念。
先看一下,下面的例子,X=College Major, Y= Likes
| College Major | Likes |
|---|---|
| Math | Yes |
| History | No |
| CS | Yes |
| Math | No |
| Math | No |
| CS | Yes |
| History | No |
| Math | Yes |
从这个表格中,可以得出:
\(H(X)=-1/2log_{2}1/2-1/4log_{2}1/4-1/4log_{2}1/4=1.5\)
\(H(Y)=-1/2log_{2}1/2-1/2log_{2}1/2=1\)
Conditional Entropy可以被定义为:
\(H(Y|X=v)\)在随机变量\(X\)已经给定值\(v\)的情况下,\(Y\)的Entropy大小,也可以解释为当两边通信端都已经了解\(X\)的值为\(v\)的时候,传输\(Y\)的时候,平均需要多少比特。所以,\(H(Y|X)\)可以被定义为:
\[H(Y|X)=\sum_{j}Prob(X=v_{j}H(Y|X=v_{j}))\]
从上面的例子可以看出:
\(H(Y|X=Math)=-1/2log_{2}1/2-1/2log_{2}1/2=1\)
\(H(Y|X=History)=0\)
\(H(Y|X=CS)=0\)
\(P(X=Math)=0.5\)
\(P(X=History)=0.25\)
\(P(X=CS)=0.25\)
\(H(Y|X)=0.5*1+0.25*0+0.25*0=0.5\)
下面我们就可以介绍一下Information Gain(信息增益)的概念。
Information Gain就是当通信两边都知道随机变量\(X\)的时候,平均每个字符可以省下多少比特。
\[IG(Y|X)=H(Y)-H(Y|X)\]
还是上面的例子:
\(H(Y)=1\)
\(H(Y|X)=0.5\)
所以,\(IG(Y|X)=1-0.5=0.5\)
Relative Information Gain (相对信息增益)就是当需要传输\(Y\)的时候,通信两边都知道随机变量\(X\)的时候,平均每个字符可以节省的比特数占总的Entropy的比例。
\[RIG(Y|X)=(H(Y)-H(Y|X))/H(Y)\]
Information Gain具体有什么用?最直接的用处就是,当有一系列输入属性(features or attributes)\({x_{1}, x_{2}, ..., x_{n}}\)与你的目标属性\(Y\)相关,可以用Information Gain来发掘哪一个输入属性,包含了较多的目标属性的信息量,也意味着这个属性可以更好的来预测目标属性。
举个例子来说,为了预测是否一个人可以活到80岁,从以往的历史数据看
\(IG(LongLife|HairColor)=0.01\)
\(IG(LongLife|Smoker) = 0.2\)
\(IG(LongLife| Gender) = 0.25\)
\(IG(LongLife| LastDigitOfSSN) = 0.00001\)
从这四个属性{HairColor, Smoker, Gender, LastDigitOfSSN的信息增益可以看出,Gender(性别)与长寿更相关。
从以上可以看出,Information Gain是一个很好的工具用来预测特定的目标,由此延伸出一个机器学习方法-Decision Tree(决策树)。
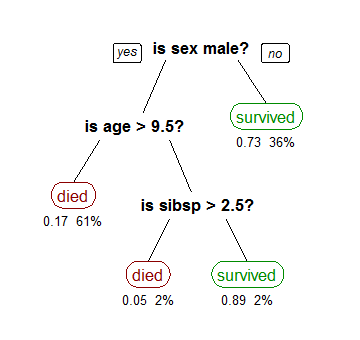
我们可以定义样本为:\((x,Y)=(x_{1},x_{2},x_{3},...,x_{k}, Y)\),其中\(Y\) 是我们试图预测的目标属性,向量\(x\)是一系列不同的属性组合而成。而决策树的目标就是创造一个模型树根据输入属性预测目标属性的值。基本思想就是先计算所有不同属性的Information Gain,既\(IG(Y|x)\)。含有最大的Information Gain输入属性就可以作为Decision Tree的根,然后这样依此递归计算Information Gain,就可以得到一个Decision Tree,如上图所示,其中树的内部节点就是输入属性,树的边就是输入属性的可能值,数的叶子就是需要预测目标属性的值。
Regerence:
Entropy, wiki, 2011
Self-Informationlecture notes of R.Victor Jones, 2011
Decision Tree Learning, wiki, 2011
克劳德.香农, 百度百科,http://baike.baidu.com/view/63224.htm
Claude Elwood Shannon,wiki, 2011
Information Gain, Andrew's tutorials, 2011





